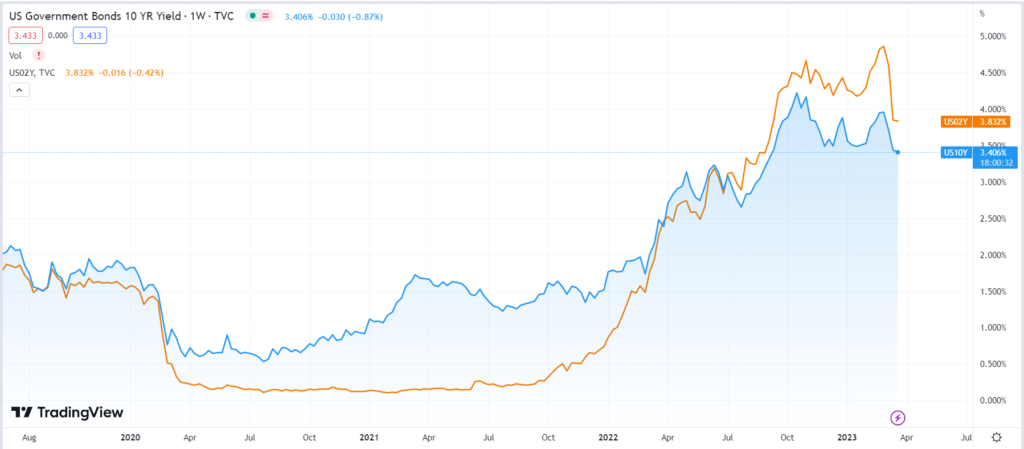
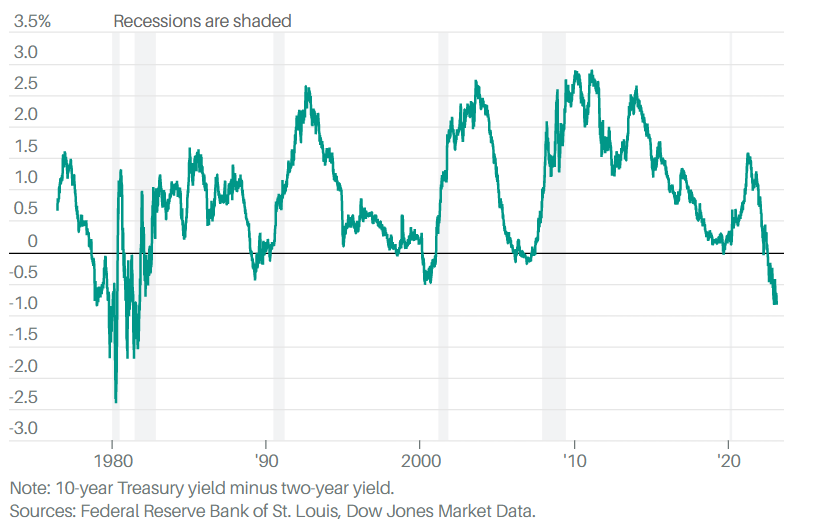
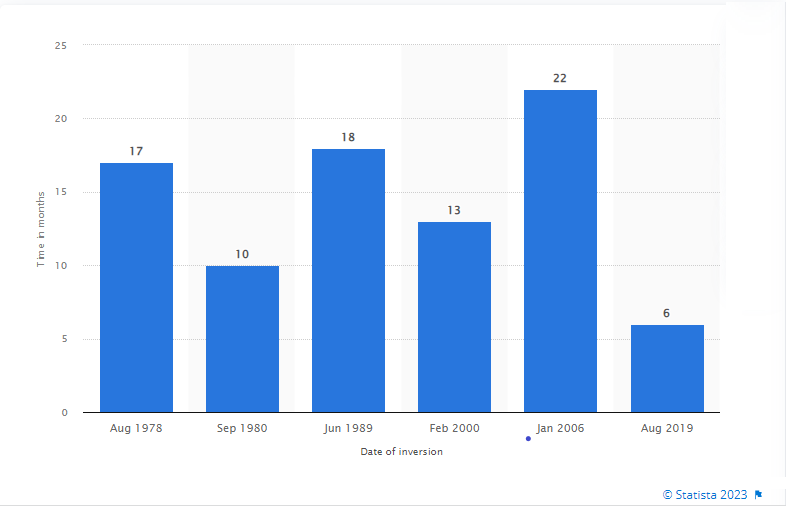
India’s export industry plays a vital role in the growth and development of the Indian economy. It’s a significant contribution to the nation’s GDP. Moreover, with India’s growing presence in the global trade market, exports have become an essential source of foreign exchange earnings.
Furthermore, exports promote entrepreneurship, innovation, and technological advancements. The Indian government has recognized exports’ importance and implemented policies and initiatives to support the industry’s growth. With India’s increasing participation in the global trade market, the future looks promising for the country’s export industry.
Indian Economy Exports in FY23 – The Forecasted Value and Factors Contributing to Growth
India’s goods and services export industry has been growing steadily over the past few years, and the latest reports suggest that the sector is set to reach new heights in FY23. The projected value of $760 billion in exports represents a significant increase from the previous years’ figures, indicating that India’s economy continues to show signs of resilience and growth.
The efforts led by Piyush Goyal, India’s Minister of Commerce, have been instrumental in driving this growth forward. Additionally, the country’s diverse manufacturing and service sectors have contributed significantly to the increase in exports.
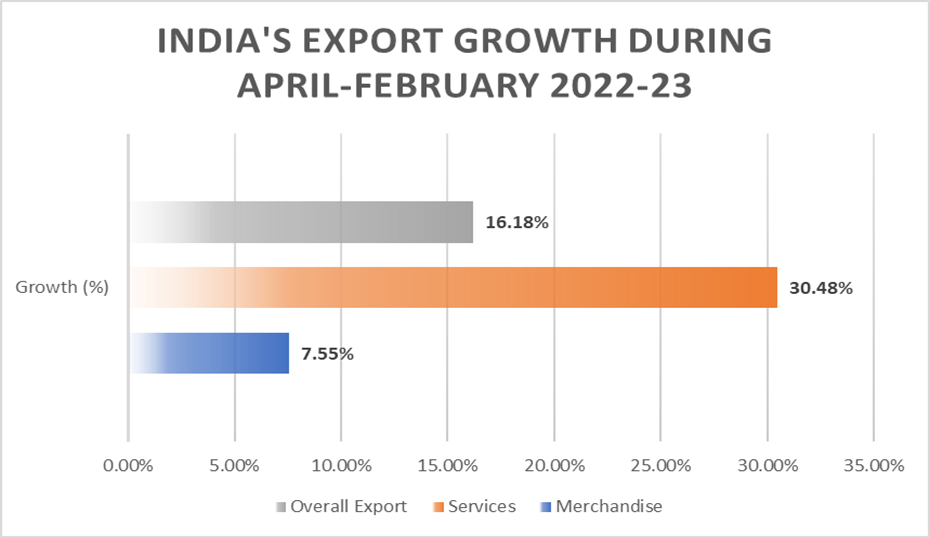
These positive figures demonstrate India’s continued potential for economic growth and present new opportunities for businesses and investors looking to tap into the country’s thriving export industry.
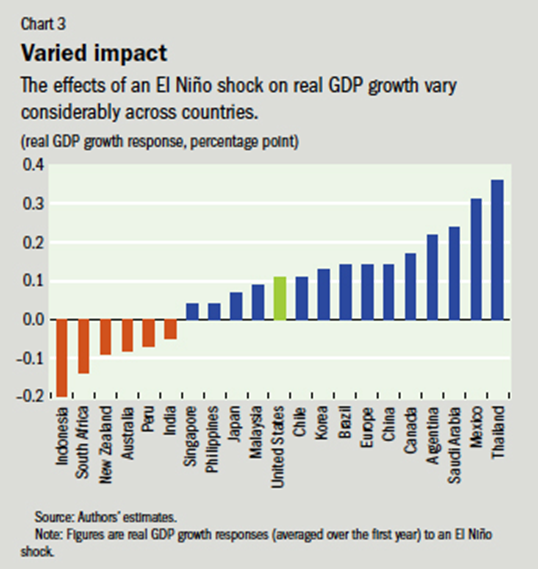
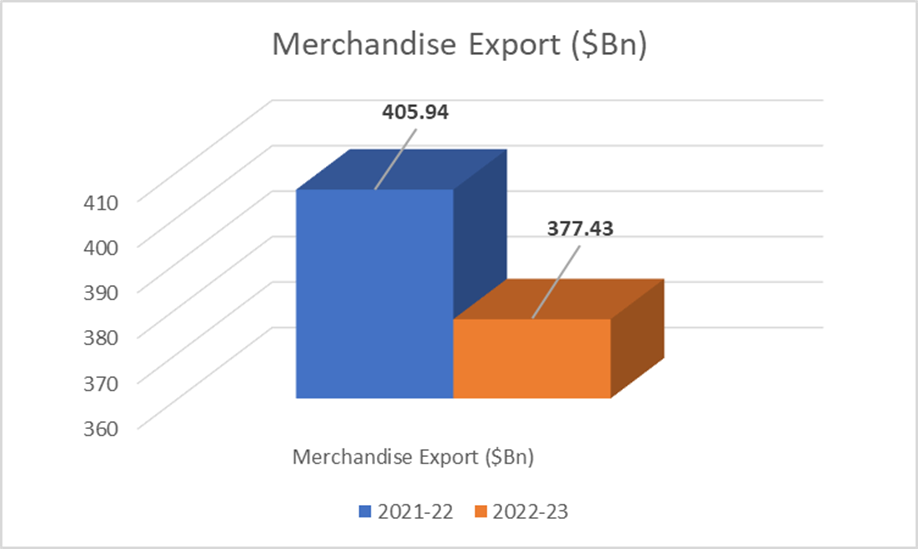
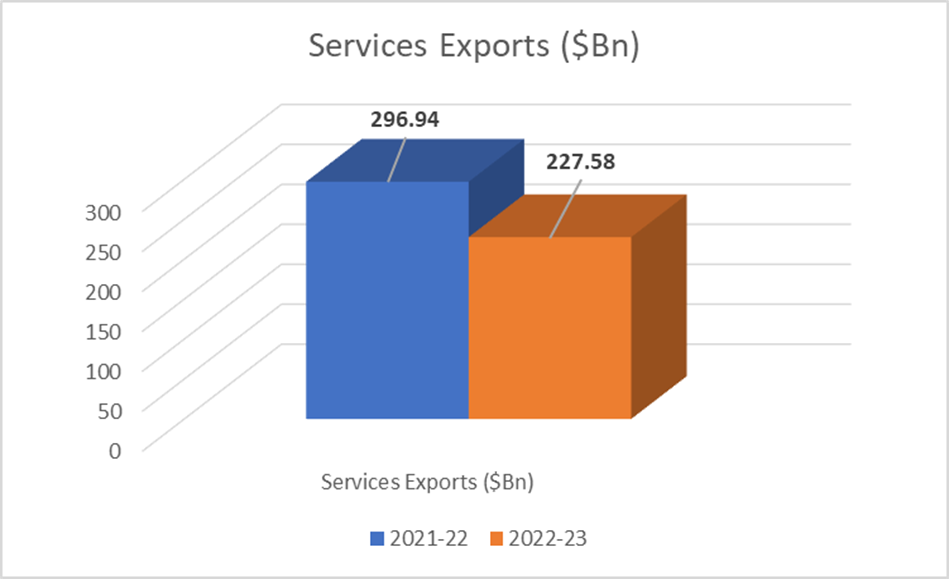
The graph below depicts progress made by both merchandise and services from April-February.
The table shows the growth rates of major sectors contributing to Indian economy exports during February 2023 and April-February 2022-23.
| Sector | February 2023 growth % | April-February 2022-23 growth % |
| Oil Meals | 220.96 | 44.12 |
| Iron Ore | 51.37 | – |
| Spices | 30.85 | – |
| Electronic Goods | 29.85 | 49.54 |
| Fruits & Vegetables | 17.42 | 11.16 |
| Gems & Jewellery | 13.76 | – |
| Rice | 11.75 | 15.88 |
| Ceramic Products & Glassware | 11.5 | 7.62 |
| Other Cereals | 10.65 | 12.15 |
| Oil Seeds | 9.4 | 13.36 |
| Cereal Preparations & Miscellaneous Processed Items | 5.22 | 16.12 |
| Marine Products | 4.96 | 3.19 |
| Drugs & Pharmaceuticals | 4.72 | 3.14 |
| Minerals Including Processed Minerals -Mica, Coal & Other Ores | 2.97 | – |
| Tobacco | – | 34.3 |
| Leather & Leather Products | – | 11.08 |
| Tea | – | 10.03 |
| Coffee | – | 8.17 |
| Organic & Inorganic Chemicals | – | 3.91 |
| Rmg of All Textiles | – | 3.28 |
According to the minister, the industry has warmly received India’s Free Trade Agreements with the UAE and Australia. Moreover, he emphasized that India’s FTAs were implemented with careful consideration and stakeholder involvement without sacrificing the quality of the agreements.
Indian Economy Exports Growth in FY23: Sector-wise Analysis and Key Drivers
The services sector plays a significant role in India’s economy, contributing more than 50% of the country’s GDP. This sector includes a range of industries such as trade, tourism, aviation, telecom, shipping, ports, communication and storage, financing, insurance, transportation, real estate, business services, software services, and IT-BPM.
The IT services and BPO industry alone employed over 4.47 million people directly and 12 million indirectly in 2020-21, accounting for approximately 8% of India’s GDP and more than 52% of the global outsourcing market. In the first half of 2020-21, the sector grew 10.8%. The tourism and hospitality services industry witnessed a remarkable recovery after the COVID-19 pandemic, with employment in the sector increasing by 48% in March 2022.
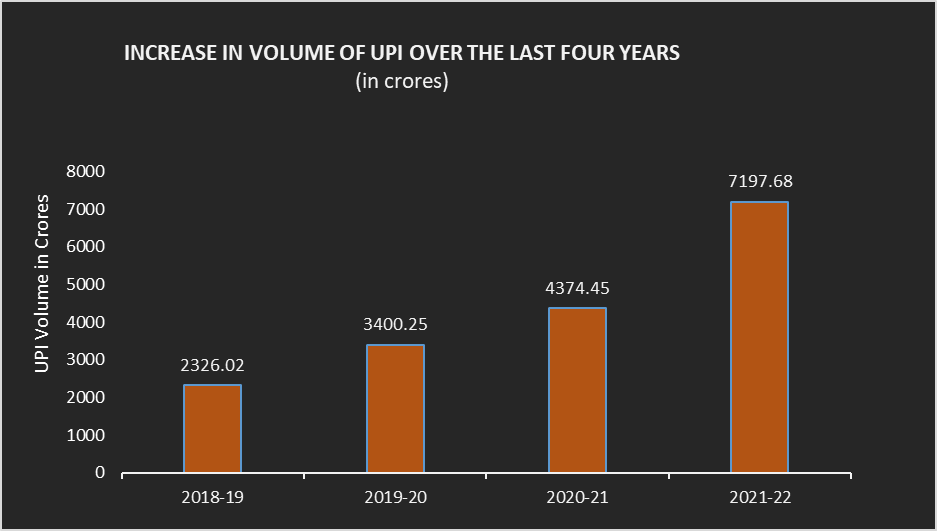
The graph below depicts the industry-wise share of total services sector exports.
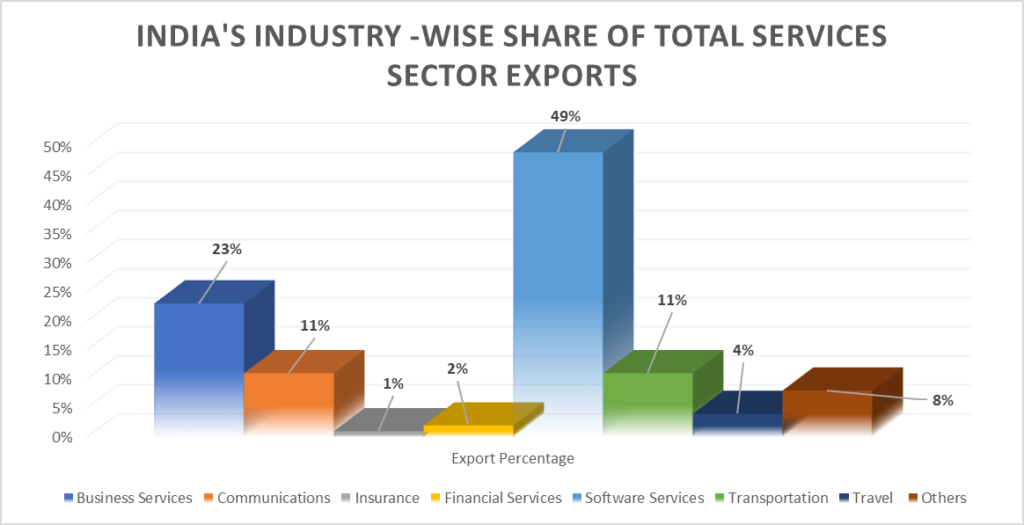
India’s economy heavily relies on exporting services, such as travel, transportation, insurance, software-IT-BPM, business services, financial services, and communication. In 2020-21, India exported services worth US$206 billion, a figure that reached the projected target of US$250 billion in 2021-22 and is predicted to reach US$325 billion by 2022-23.
- In 2021-22, India’s services exports generated a trade surplus of US$105.2 billion, a significant increase of 24% from 2019-20.
- The services sector in India is the leading recipient of FDI inflows, with India being the fifth-largest recipient worldwide.FDI inflows into the industry totalled $16.73 billion in the first half of 2021–2022, accounting for 54% of all FDI into India.
- One of the industries that received the most FDI was the computer software and hardware services sector, which in 2021–2022 received roughly 25% of all FDI into India. India’s overall FDI inflows for the same period were $83.57 billion.
Indian Economy Exports Top Services: Dominance in IT, Software and BPO Industries
India’s services, including software, computer, IT, BPO and call centres, are exported to many parts of the world, with the USA, the UK, and Japan being the largest importers. The availability of a large workforce, cheap labour, and English language skills makes India’s services popular worldwide.
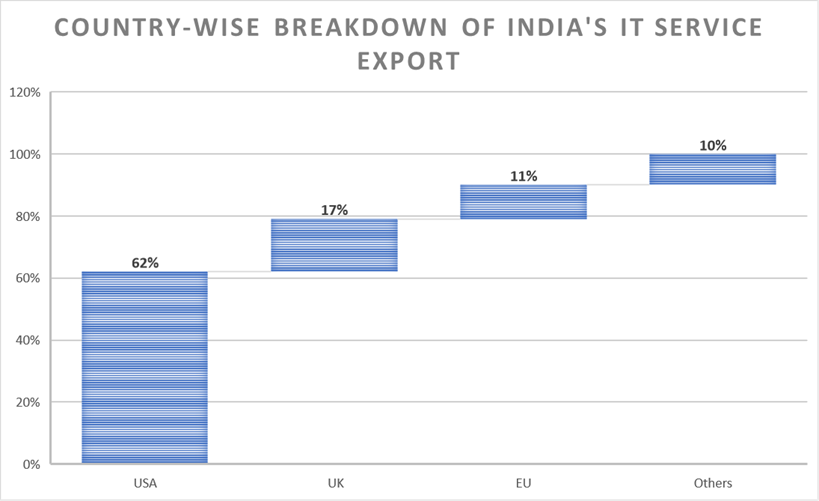
During 2020-21, the USA and Canada imported $75 billion of software services from India. Other significant software service importers are Canada, Asia, Australia, and New Zealand. Other key export markets for India include Hong Kong, Singapore, Germany, Bangladesh, the Netherlands, and Nepal.
Indian Economy Exports: Government Initiatives
The Indian government has launched several initiatives to boost service exports, such as the Service Export from India Scheme (SEIS), Software Technology Park (STP) Scheme, Digital India Internship Scheme, and the PhD Scheme.
Additionally, the government is promoting trade deals with various countries, engaging with states, and implementing schemes like PLI, RoDTEP, and Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti’s plan to achieve the target of making India a $5 trillion economy by 2025. The Export Preparedness Index (EPI) and LEADS have also been launched to evaluate state export readiness.
Indian Economy Exports: Challenges and Outlook
India faces challenges such as improving infrastructure and ease of business, but it also has opportunities to grow exports and achieve economic targets. India can leverage its skilled labour, diversify exports to new markets, and focus on product quality, innovation, and branding to overcome competition in the global market.
The government’s initiatives, such as the PLI scheme and recent trade agreements, support domestic manufacturing and greater market access to Indian products.
Final Words
In conclusion, India’s export industry plays a crucial role in the country’s economic growth and development. The sector shows promising growth and resilience, with diverse industries contributing to its success.
FAQs
Which crop is India’s largest exporter?
During 2021-22, rice accounted for over 19% of India’s total agricultural exports, making it the most important agricultural product exported from India.
Who handles exports in India?
The Central government exercises the powers conferred by section 5 of the Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act 1992 to notify the Foreign Trade Policy, which regulates exports and Imports.