Bank failures can significantly impact depositors, so it’s crucial to understand how to safeguard your savings. Recent news and the experiences of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank failures serve as a reminder of the importance of being prepared.
In this article, we’ll explore tips for protecting your savings from bank failures, including choosing a reputable bank, diversifying your accounts, and monitoring them regularly. We’ll also discuss the role of the FDIC and the benefits of FDIC insurance. Don’t let a bank failure catch you off guard; read on to learn how to keep your money safe.
Bank Failures: Causes and Help Available To Depositors
Understanding bank failures is crucial in protecting your savings. It refers to the inability of a bank to meet its financial obligations to depositors.
Causes of failures include
- Poor management,
- Economic downturns, and
- Fraud
When a bank fails, depositors may lose access to their funds, significantly impacting their finances. In such cases, it may not have sufficient funds to repay all of its depositors, leading to losses for those with uninsured deposits. In the US, the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) plays a crucial role in protecting depositors. The FDIC provides deposit insurance to protect depositors’ funds in case of failures.
However, in India, the State owns a majority of bank assets which works as an implicit assurance of safety for their depositors. For other banks, the government has willingly and compulsively bailed out troubled banks and FIs via forced mergers or regulatory forbearance and unconventional regulatory engineering. It happened in the case of the Punjab and Maharashtra Cooperative (PMC) Bank bailout too.
India has managed to protect the interests of depositors in the three instances of bank failures that occurred within the past three years, namely PMC Bank, YES Bank, and Laxmi Vilas Bank. The regulatory body has succeeded in doing so with the government’s support. Moreover, software companies have also been prevented from failing in response to the public’s demands.
History of Bank Failures in the US
Bank failures have been a recurring issue in US history, as illustrated by a graph depicting the number between 1984-2023.
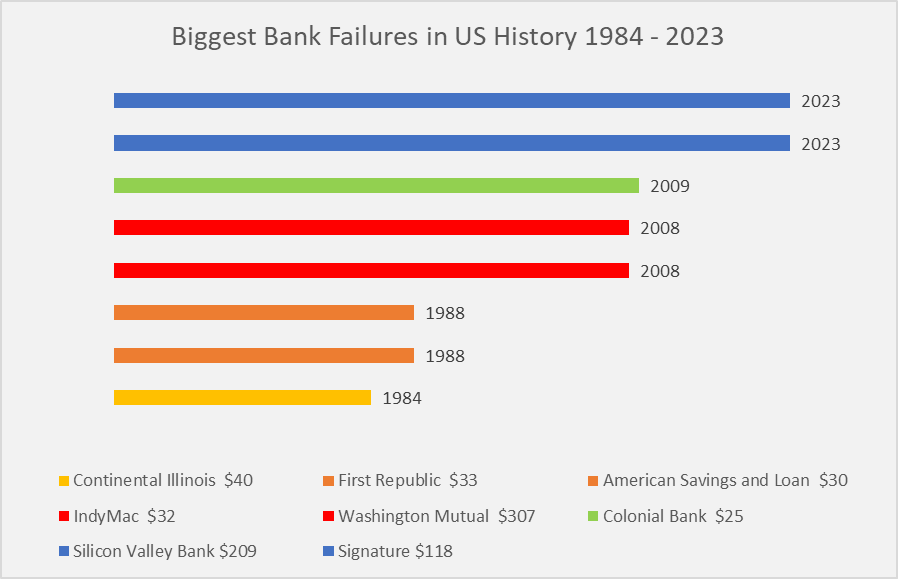
Bank Failures: Consequences and Impact on Depositors
Inaccessible Funds: The moratorium that suspends bank operations for an uncertain period can be challenging for customers, especially small depositors, as their funds become inaccessible, despite deposit insurance guaranteeing eventual repayment. Though the proposed Banking Resolution Corporation aims to provide formal mechanisms for quickly liquidating banks, it has yet to become a reality.
Increase in Fees & Interest: Bank failures can have severe consequences beyond just hurting depositors and investors. They can also result in increased fees and interest rates as banks attempt to make up for their losses.
Slow-down in Lending: One bank’s failure can trigger a chain reaction of other failures, causing a significant slowdown in lending and negatively impacting the economy. So the central banks would want to avoid dealing with such a crisis.
DICGCI: The Key Player in Protecting Your Savings in India
Deposit insurance, an instrument that helps to minimize the impact of bank failure, has been used sparingly in India. The banks themselves have long funded deposit insurance in India. Banks’ contributions are, however, not ‘risk-priced.’
Under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Act, all banks must pay the same premium to insure their deposits, regardless of their financial health or asset quality. However, a few strong banks have been reluctant to fulfill this requirement.
FDIC: The Key Player in Protecting Your Savings from Bank Failures
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation is an independent government agency that provides deposit insurance to protect depositors in case of bank failures. FDIC insurance coverage applies to deposits in savings accounts, checking accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs) at FDIC-insured banks.
The coverage limit is currently $250,000 per depositor per insured bank, and it covers both principal and any interest earned. The primary benefit of FDIC insurance is that it protects depositors against the risk of losing their money if their bank fails.
If a bank fails, the FDIC takes over it and ensures that depositors receive their insured funds, usually within a few business days. The U.S. government fully backs FDIC-insured deposits, making them one of the safest places to keep your money.
It means that even if your bank fails, you can still recover your insured funds up to the coverage limit. It’s important to note that not all banks are FDIC-insured, and depositors should always check to ensure their bank is FDIC-insured before opening an account.
The FDIC maintains a database of FDIC-insured institutions on its website, and depositors can also look for the FDIC logo on bank websites, statements, and marketing materials. By choosing an FDIC-insured bank and understanding the benefits of FDIC insurance, depositors can safeguard their savings from bank failures and other financial risks.
Silicon Valley and Signature Bank: Lessons from Their Failures
Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank are two examples of banks that have experienced significant failures, leading to financial losses for their customers. These failures highlight the importance of safeguarding savings from bank failures.
In the case of Silicon Valley Bank, the bank’s failure was due to a combination of factors, including poor risk management and the bank’s exposure to high-risk loans. The failure of Signature Bank, on the other hand, was due to the bank’s heavy reliance on volatile funding sources.
These cases offer valuable lessons for customers of any bank.
It’s essential to understand the potential risks and to safeguard savings, including diversifying accounts, choosing a reputable bank, monitoring accounts regularly, and being aware of FDIC coverage limits.
By taking these steps, customers can better protect themselves from the impact of any future bank failures.
Bank Failures: Safeguarding Your Savings
- To safeguard savings, it is important to diversify your accounts, choose a reputable bank, monitor your account regularly, and be aware of FDIC coverage limits.
- Diversification of accounts is one of the most effective ways to protect your savings. Instead of keeping all your funds in a single bank account, consider spreading them across multiple banks or financial institutions.
- Choosing a reputable bank is crucial to safeguarding your savings. Look for banks with a solid financial standing and a proven stability and reliability track record.
It’s also important to monitor your account regularly to detect any suspicious activity or errors. Be sure to review your account statements and balance frequently and report any discrepancies to your bank immediately. By following these tips and being aware of FDIC coverage limits, depositors can minimize the risks of financial losses in the event of a bank failure.
Final Words
Safeguarding savings from bank failures is crucial to prevent financial losses. Recent examples of bank failures are a reminder to diversify accounts, choose reputable banks, monitor accounts regularly, and depositor insurance coverage limits.
FAQs
How to confirm if my bank is FDIC-insured?
You can check if your bank is FDIC-insured by looking for the FDIC logo or using the FDIC’s BankFind tool on their website.
What happens to my money if my bank fails and is not insured?
If your bank is not insured and it fails, there is no guarantee that you will get your money back. You should always make sure your bank has appropriate insurance to protect your savings.